Whenever we get sick, we always try to recover from it as soon as possible.
One of the most essential components in that recovery process is Vitamin C.
This essential vitamin plays a crucial role in the overall health and wellness of the body, especially its ability to stimulate the immune system to help fight infection.
In this article, we’ll be discussing two main Vitamin C benefits: its antioxidant properties, and its immune system boosting effects.
But first:
What is Vitamin C?
Did you know that cats, dogs, and even goats can create Vitamin C within their own bodies, while humans, bats, and guinea pigs cannot?
Humans cannot self-produce Vitamin C because of mutations in the L-gulono-γ-lactone oxidase gene, or the GULO gene, that have rendered it non-functional. The GULO gene is responsible for encoding an enzyme that acts as a catalyst for the last step in the biosynthesis of Vitamin C.
But what is this vitamin, and why is it so important?
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbate and ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that is naturally found in various foods, or is added or fortified to other foods. Vitamin C also is commonly sold as a dietary supplement. It is because of our inability to self-produce Vitamin C within our bodies that we have to rely on our diets and supplements in order to get sufficient amounts of this essential nutrient.
Vitamin C is such a potent antioxidant that it helps the immune system fight off many types of diseases and infections, from the flu and the common cold, to more serious and life-threatening diseases, such as heart disease. In its dual role as an antioxidant and immune system booster, Vitamin C plays a crucial role in many important bodily functions.
Let’s take a look at:
What Makes Vitamin C Such a Potent Antioxidant?
A lot of the human anatomy depends on the flow of electrons between molecules. Free radicals are molecules that have been rendered unstable due to having an unpaired valence electron.
For reference:
Valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell surrounding the nucleus that determine an element’s chemical properties, and whether that element can bond with others.
Free radicals are catabolic in nature, which means that they help break large molecules down into smaller ones.
Free radicals are made in a cycle known as oxidative stress, which causes harm to the cells and destabilizes them, as well as bodily tissues and organs.
Here is where Vitamin C fits in.
Vitamin C helps combat oxidative stress with its strong ability to donate electrons to neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidation in proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
Additionally, Vitamin C has been shown to regenerate or restore other antioxidants within the body, including Vitamin E in the form of alpha-tocopherol.
Vitamin C regenerates Vitamin E by reducing the newly formed tocopheryl radicals through the donation of a hydrogen atom. Vitamin E radicals, called tocopheryl radicals, are formed when Vitamin E scavenges oxygen radicals.
It’s a lot of terminology, we know, but bear with us.
Oxygen radicals are unstable molecules containing oxygen that easily react with other molecules in a cell. They are naturally formed during the process of cellular respiration, and as intermediates of many enzymatic reactions.
However, overaccumulation of oxygen radicals may damage DNA, RNA, and proteins, and could cause cell death.
What About the Immune System Boosting Function of Vitamin C?
Vitamin C benefits the immune system, boosting function in the body in many different ways.
For example, Vitamin C is a cofactor for enzymatic reactions related to the biosynthesis of catecholamine hormones.
Catecholamines help the body respond to stress or fright, prepare it for “fight-or-flight” reactions, and regulate the heartbeat, breathing rate, as well as other physiological functions.
Norepinephrine is one of the most important catecholamine hormones in the body.
Vitamin C also acts as a cofactor in the enzymatic reactions related to the biosynthesis of amidated peptide hormones.
Amidated peptides are peptides that end with an amide group instead of a carboxyl group.
So why is this important?
The process of amidation both enhances the biological activity of peptide hormones, and prolongs their half-life in the bloodstream.
These hormones are crucial to the cardiovascular response to severe infection.
Vasopressin is an example of an amidated peptide hormone.
Vitamin C has also been demonstrated in numerous studies to be essential to wound healing.
This is due to Vitamin C’s decreasing the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and increasing the expression of various wound healing mediators.
There have been experiments done with fibroblast cell cultures, which are the primary active cells of connective tissue within the dermis layer that allow the skin to recover from injury.
These studies have suggested that Vitamin C can alter the gene expression profiles of fibroblast cells to promote their proliferation and migration, which is crucial for reconstructing skin tissue and wound healing.
But wait, there’s more!
Additionally, Vitamin C is believed to influence many essential aspects of neutrophil function.
Neutrophils are white blood cells that protect the body from infection, and make up 40%-60% of all white blood cells in the body.
Their role in fighting infection is by ingesting microorganisms, as well as releasing enzymes to kill them.
Vitamin C helps neutrophils migrate in response to inflammatory mediators.
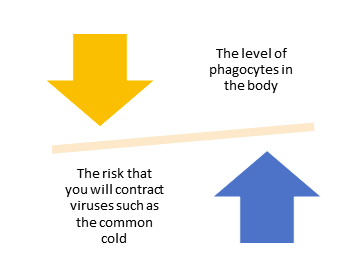
It also helps bring on the process of phagocytosis, in which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dying or dead cells, as well as kill microbes.
Neutrophils are a type of phagocyte.
Additionally, Vitamin C helps induce apoptosis, a process of programmed cell death that helps remove cells during development, gets rid of potentially virus-infected and cancerous cells, and helps maintain balance in the body.
Furthermore, Vitamin C helps macrophages, which are another type of phagocyte that ingests foreign substances, microbes, and cancer cells, clear away apoptotic cells.
In helping bring about the processes of apoptosis and clearance by macrophages, Vitamin C helps protect host tissue from excessive damage.
Next, let’s take a closer look at:
What Kind of Cells Are In The Immune System?
Before discussing how Vitamin C affects different bacteria and diseases, it is important to explain the different types of cells in the immune system.
There are two main types of cells: phagocytes and lymphocytes.
Phagocytes include:
- Neutrophils
- Macrophages
- Monocytes
- Dendritic cells
- Mast cells
These cells are ultimately responsible for coordinating the innate immune response, which means that they trigger non-specific responses to specific foreign pathogens.
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell that travels into the tissues and organs, which are differentiated or converted into a macrophage or myeloid lineage/bone marrow tissue dendritic cell.
Dendritic cells are a type of immune cell that processes and presents antigens on its surface to T-cells.
Mast cells a type of immune cell that mediates inflammatory responses such as allergic reactions and hypersensitivity.
Next, let’s look at lymphocytes.
Lymphocytes include:
- B-cells
- T-cells
- Natural killer cells
B-cells are white blood cells that are responsible for producing antibodies to fight antigens.
T-cells are white blood cells that either help other immune cells, or kill infected cells and tumors.
Natural killer cells are white blood cells that kill infected cells or tumors according to the innate immune response.
Whereas natural killer cells are part of the innate immune system, B-cells and T-cells are part of the adaptive immune system, which triggers specific responses to specific foreign pathogens.
B-cells and T-cells also leave behind memory cells that remember specific pathogens in order to coordinate a strong and fast response if they are found again.
This process is essential to adaptive immunity.
Now that we know more about the immune system, let’s discuss how Vitamin C benefits the immune system in treating infections.
How Effective Is Vitamin C in Treating the Common Cold?
Although colds themselves are not so dangerous, they are dangerous in the sense that they may serve as early signs of immunodeficiency, which is a state in which the body’s ability to fight infectious disease is compromised, or totally absent.
As a result, immunodeficiency leaves you vulnerable to various infections.
For older adults, especially, the cold can lead to pneumonia and other respiratory infections.
There has been extensive research done on how Vitamin C benefits the common cold.
Many studies have shown that Vitamin C is able to not only reduce the incidence of colds, but also their duration and severity.
More recent research has suggested that the usage of higher doses of Vitamin C is able to reduce the incidence of colds.
Harri Hemilä, M.D., Ph.D., currently works at the Department of Public Health at the University of Helsinki, and specializes in Infectious Diseases and Immunology, as well as Vitamin C and the common cold.
He has done his own studies and analyses, as well as reviewed those done by other researchers, on the relationship between acute respiratory infections and Vitamin C.
In one such review that he conducted, he examined recent research regarding the connection between Vitamin C and infections.
Dr. Hemilä believes that there is strong evidence to suggest that Vitamin C may decrease the incidence of the common cold in special conditions and/or among certain groups of people.
In five random-controlled trials, the participants were under conditions of heavy, short-term physical stress and hot or cold environments.
Vitamin C supplements in amounts of at least 200 mg daily halved the incidence of the common cold in these participants.
Stress produces a lot of effects in the body that decreases its immune system response.
When the body experiences stress, the number of lymphocytes decreases.
Additionally, with increased stress comes increased production of cortisol.
However, if the levels of cortisol remain elevated for a prolonged period of time, then the body may be at risk for further inflammation.
Chronic inflammation means that the immune system is too overworked and overwhelmed to protect the body from infection.
In an unrelated study that was published in the Nutrients journal, researchers examined the effects of Vitamin C supplements on physical activity and respiratory tract infections during the peak of the common cold season.
This study was a randomized, double-blind controlled trial that lasted for 8 weeks. The participants were men in the age range of 18-35 years old with a marginal Vitamin C status of less than 45 micromol per liter.
Vitamin C status of less than 23 micromol per liter is deficient, whereas 23-50 micromol per liter is suboptimal. These plasma levels of Vitamin C represent insufficient antioxidative function.
The results?
Thirteen of the men received a placebo. Eleven of these men reported a cold during the study period.
The other fifteen men received daily Vitamin C supplements of 1,000 mg. Only seven of these men reported a cold during the study period.
The cold duration of the men in this group was decreased by 59% compared to the group of men who received the placebo. This reduction meant 3.2 fewer days of having a cold.
Why is that?
The researchers believed that this was due to either Vitamin C enhancing the activities of immune cells known as natural killer cells, or improving the movement of white blood cells called lymphocytes in response to an infection.
So what about physical activity then?
During weeks 5-6 of this trial, the men in the Vitamin C group showed a 21.2% greater physical activity score than the men in the placebo group.
During weeks 7-8 of this trial, the men in the Vitamin C group showed a 39.6% greater physical activity score than the men in the placebo group.
This improved physical activity score may be due to Vitamin C’s antioxidant properties in fighting oxidative stress that comes from fatigue, as well as its neuroprotective properties, which influence the oxidative fuel supply in the brain for a sense of well-being.
In fact, the antioxidant and antihistamine properties of Vitamin C have also been linked to the relief of cold symptoms. This is because oxidative stress and histamine aggravate the severity of the cold.
Overall, this study further supports the benefits of Vitamin C supplementation in men who have adequate, if not low levels of Vitamin C.
How Effective Is Vitamin C in Treating the Flu?
Now, let’s take a look at how Vitamin C benefits the flu.
One highly cited research study from 1999 investigated the effectiveness of mega dose-Vitamin C in preventing and relieving flu and common cold symptoms.
The researchers of the study tracked the number of reports of common cold and flu symptoms among the 1990 control group of 463 students from the technical training facility, and compared them with the reports of the 1991 test group of 252 students from the same facility.
The participants in the control group were treated with pain relievers and decongestants.
The test group participants were treated with hourly doses of 1,000 mg of Vitamin C during the first six hours, and then three times daily after that.
The participants in the test group who did not report any flu or common cold symptoms were also administered 1,000 mg doses of Vitamin C three times daily.
Overall, it was found that, in the test group, the common cold and flu symptoms that were reported were reduced by 85% compared to the control group.
This reduction was seen after the participants in the test group received their mega dose of Vitamin C supplement.
It was concluded that megadose Vitamin C supplement, whether before or after the common cold and flu symptoms appeared, helped relieve and prevent those symptoms in the test group compared to the control group.
At the time of publication, the researchers stated that, for more than 30 years, Vitamin C supplements in mega dose amounts was recognized as an effective agent against the common cold and flu.
Liposomal Vitamin C Supplements Further Increase Vitamin C Benefits
If you are looking for ways to increase your Vitamin C blood levels, you should definitely consider a Liposomal Vitamin C supplement.
More specifically, you may want to do some research on Liposomal Vitamin C Technology.
Liposomal Vitamin C Technology uses micro sized fluid filled liposomes to protect and deliver nutrients directly into the cells and tissues of the body.
These liposomes are very similar to human cells, which makes it easier for them to be transported within the body.
As a result, nutrient absorption is greatly increased, and there is less intestinal discomfort than with using standard oral melatonin supplements.
Liposomal Technology provides several different advantages, including:
- Micro-sized encapsulation that protects against the harsh acidity of the gastrointestinal tract
- Increased delivery to cells, tissues, and organs
- Higher absorption rates and bioavailability than other standard oral supplements
- Noninvasive compared to intravenous supplementation
- Lower doses provide the same effects as high-dose standard oral supplements
- Helps put nutrients to use by the body faster
- Prevents gastrointestinal distress usually experienced with standard oral supplements
One study was able to demonstrate that Liposomal Vitamin C supplement has greater bioavailability than standard oral Vitamin C and avoids its common side effect of gastrointestinal distress.
Liposomal Vitamin C supplement also avoids the disadvantages of intravenously delivered Vitamin C, such as high cost, availability, and inconvenience.
Clearly, Liposomal Vitamin C supplements deserve serious consideration for its potential potent antioxidant and immune-boosting benefits.
Why You Should Consider a Vitamin C Supplement?
Vitamin C is essential to the body for its potent antioxidant and immune-boosting properties.
It helps stimulate immune cells to fight infections such as the common cold and flu, relieving your symptoms and helping you recover from the infections faster.
You should take the necessary steps to keep your levels of Vitamin C within a healthy range to keep your immune system strong and ready to fight infections.