Detoxification has become more popular than ever. Many people have started to follow specific diets and use certain products to help detoxify the body. While our body is equipped to detoxify on its own, we can always optimize its natural detoxification system. After all, our modern world is full of toxins that overburden our body’s detoxification abilities.
Melatonin is a CRUCIAL component of this natural detoxification process.
In this article, we’ll be discussing the ways in which the body detoxifies itself, and how melatonin plays an important role.
Detoxification 101: The Essential Guide
Detoxification refers to the process of eliminating toxins. Detoxifying the body is essential to prevent chronic sickness and illness.
Many organ systems are involved in this process in the body:
- Skin
- Digestive System
- Lungs
- Lymph Nodes
- Liver
- Kidneys
When it comes to the skin, the act of sweating opens the body’s pores through which toxic chemicals and heavy metals are released. Research has suggested that sweating is a safe and effective way to eliminate the heavy metals of mercury, lead, arsenic, and cadmium from the body.
The toxins that come from eating or drinking can pass through the digestive system and be removed from the body in feces. In fact, when you have food poisoning, the body has a self-defense mechanism of inducing vomiting and diarrhea to quickly get rid of toxins.
The lungs help get rid of toxic gases and volatile chemicals that may be breathed out of the body, such as the chemical acetaldehyde, a product of alcohol metabolism. Your lymph nodes work together with your cardiovascular system to help flush toxins out of the body by carrying them away from the tissues and into the bloodstream, where they are then detoxified by the spleen. The lymphatic system is essentially an extensive drainage network that helps defend the body from infections.
That brings us to the two most important organs involved in detoxification:
The liver and the kidneys.
In short, liver detoxification focuses on converting toxins into either non-toxic substances, or substances that can be easily removed from the body.
The kidneys filter out waste products from muscular metabolism, urea, the main organic component of urine from protein metabolism, excess fluids, bacteria, and toxins.
What Is Melatonin?
Melatonin is known as the “sleep hormone.”
It is produced by the pineal gland, located in the center of the brain. Although inactive during the daytime for most people, it actively starts producing melatonin during the nighttime, while in darkness.
From there, melatonin is gradually released into the bloodstream.
Countless studies have shown that melatonin has many sleep benefits:
- Puts you into a state of drowsiness to get you ready for sleep
- Helps you fall asleep quicker
- Extends your total sleep duration
- Enriches your overall sleep quality
- Enhances your alertness in the morning
- Treats sleep issues caused by insomnia or jet lag
During a normal night of sleep, blood levels of melatonin will stay higher between the hours of 9 PM – 9 AM for a period of about 12 hours. As the sun rises and daylight comes, the pineal gland will become inactive, and the blood levels of melatonin will decrease to a point that they are barely detectable.
How Melatonin Detoxifies the Brain
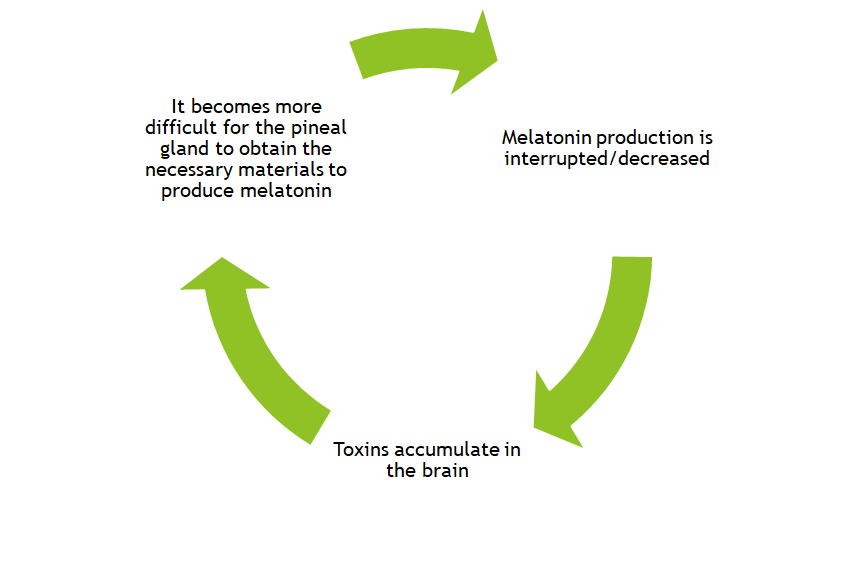
The Negative Cycle of Melatonin Deficiency
We are constantly exposed to numerous toxic substances that our natural detoxification systems have not adapted to. When we have deficient levels of melatonin in the brain, we begin to accumulate metabolic waste and poisonous toxins from the environment. That is because the brain cannot detoxify itself at the same rate as it absorbs unnecessary waste and toxins. Whenever there’s an excessive amount of contaminants that the body cannot detox, the body becomes more vulnerable to infection and disease.
Over time, cognitive function declines in a progressively noticeable way with symptoms including:
- Insomnia
- Anxiety
- Brain fog
- Memory loss
- Depression
When cognitive impairment is serious enough, that may be a sign that you have developed neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
So, where does melatonin fit into all of this?
Deficient levels of melatonin is just one of many possible sources of these symptoms. Even when these symptoms are due to an unrelated cause, a deficiency in melatonin will only make these symptoms worse.
This marks a cyclical effect:
This will steadily continue up to the point at which the brain has become poisoned and unable to naturally detoxify without outside assistance.
How Mastication Detoxifies the Brain
This leads the brain to turn to the second method by which it revivifies itself: the brain initiates teeth grinding and mashing during nighttime.
You may wonder, how does that help?
The body is attempting to forcibly remove the toxic substances by working the jaw, which increases the pumping force on the skull.
There is scientific evidence to support this idea.
According to Japanese researchers in a 2008 study called, “The masticatory organ and stress management,” when a person clenches or grinds their teeth, this helps produce natural stress-fighting chemicals in the brain.
This function is believed to be important in helping alleviate stress-induced psychosomatic disorders by:
- Reducing or suppressing the response of the limbic system to a stimulus: The limbic system is the area of the brain that regulates emotions, memories, and arousal or stimulation, as well as other important functions.
- Reducing or suppressing the response of the autonomic nervous system to a stimulus: The autonomic nervous system is the part of the nervous system that controls and regulates the internal organs in an unconscious manner.
- Reducing or suppressing the response of the HPA axis to a stimulus: The HPA axis drives the stress response to chronic stress.
Additionally, the researchers’ findings strongly suggest that teeth clenching and grinding is able to reduce stress-induced allostatic overload.
What does that mean?
Well, allostasis refers to the body’s attempt to adapt to stressors by modifying all physiological parameters, such as blood pressure or hormone production, in order to restore stability.
Allostatic overload occurs when the body’s adaptive response is prolonged and physiological parameters are repeatedly modified, or the adaptive response is improperly managed.
So, teeth clenching and grinding help reduce the body’s state of exhaustion from trying to adapt to stress.
When melatonin production normalizes, the brain sends a signal to the masticatory system, which is the set of organs and structures involved with chewing, clenching, and grinding, to stop doing those actions.
The brain is then able to resume its regular nutrient uptake and waste disposal.
The Antioxidant Benefits of Melatonin
How else does melatonin help detoxify the brain?
Well, according to research published in the Current Neuropharmacology journal, oral melatonin is readily available to the brain and counteracts different processes occurring during aging and age-related neurodegenerative disorders.
These processes include:
- Oxidative stress & damage
- Acute & chronic inflammation
- Loss of neural regeneration
The brain is especially vulnerable to free radical damage because of its high concentrations of polyunsaturated fatty acids and transition metals, and low concentrations of cytosolic antioxidants.
For reference:
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are healthy, beneficial fats in the body and include essential fatty acids such as omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 families.
Transition metals are involved in the production of reactive oxygen species, or oxygen radicals. Transition metals include iron, copper, cobalt, chromium, and molybdenum.
Oxygen radicals are unstable molecules containing oxygen that easily react with other molecules in a cell.
They are naturally formed during the process of cellular respiration and as intermediates of many enzymatic reactions. However, overaccumulation of oxygen radicals may damage DNA, RNA, and proteins, and may cause cell death.
Cytosolic antioxidants refer to antioxidants that affect the cytoplasm, or intracellular fluid, in a cell.
Back to melatonin:
Countless studies have shown that melatonin:
- Acts as a free radical scavenger
- Stimulates other intracellular antioxidant activity
- Inhibits the expression of iNOS, an enzyme involved in the production of nitric oxide, which is an important cellular signaling molecule: This leads to the decrease in the levels of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species, another type of free radical that contains nitric oxide.
Other studies have shown that the administration of melatonin helps prevent nitrosative stress, caused by inflammation, within brain mitochondria. Nitrosative stress is similarly toxic to oxidative stress and occurs when nitric oxide reacts with oxygen.
This all sounds good, but:
Does melatonin have any benefit in people suffering from neurodegenerative disorders?
Melatonin has also been shown to prevent cognitive decline in mice with Alzheimer’s disorder. In particular, their working memory, spatial reference memory, and basic mnemonic function were maintained.
In regards to Parkinson’s disease, melatonin has been shown to protect against neuronal damage and loss from overstimulated neurotransmitters.
It does so by decreasing the amount of autoxidation of dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved with experiencing happiness and pleasure. Dopamine autoxidation results in the formation of various reactive oxygen species.
Melatonin has shown the ability to significantly reduce apoptosis, a type of programmed cell death when it was experimentally induced.
Liposomal Melatonin Optimizes the Benefits of Melatonin
The toxins that are especially dangerous to the neurons and glia are those that are able to go through the blood-brain barrier.
For those of you who don’t know:
Glia are the non-neuronal cells of the central nervous system that help ensure that neurons are functioning properly. Some glial cells are believed to influence how we process information.
These toxins cause the production of free radicals within the cell and mitochondria, which leads to the oxidation of lipids, proteins, DNA, and other essential macromolecules.
When such oxidative and nitrosative stress is severe enough, it can lead to apoptosis of neurons and glia, which may impair your motor, sensory, cognitive, and psychological functioning.
The antioxidant benefits of melatonin in protecting the brain from neurotoxins are enhanced by the ability of melatonin to readily pass through the blood-brain barrier.
Liposomal technology uses micro sized fluid filled liposomes to protect and deliver nutrients directly into the cells and tissues of the body.
They are formulated for increased absorption and bioavailability, which is helped by the micro sized liposomes being able to pass through the blood-brain barrier.
What does this mean?
Liposomal melatonin is optimized for passing through the blood-brain barrier and delivering high-dose amounts of melatonin for faster usage by the brain to protect itself against oxidative and nitrosative stress and damage.
Why You Should Supplement Liposomal Melatonin for Improved Brain Detoxification
Liposomal technology helps ensure that melatonin can go through the blood-brain barrier and put its antioxidant and free radical scavenger effects to work.
Melatonin may help protect the brain from further cognitive decline in age-related neurodegenerative disorders. It also helps with stress relief and shielding the brain from free radicals that it is especially vulnerable too.
Clearly, melatonin is greatly beneficial to brain health and the general wellness of the central nervous system.